Google is rolling out the Imagen 2, which stands out for its high-quality, photorealistic outputs that closely match user prompts. Initially available to Google Cloud customers leveraging Vertex AI and approved for access, Imagen 2 boasts significant enhancements over its predecessor.

Developed using Google DeepMind's advanced technology, Imagen 2, quietly launched during Google's I/O conference in May, promises remarkable improvements in image quality. Google claims it is now capable of rendering text and logos, opening up possibilities for diverse applications such as advertising. Google Imagen 2 stands alongside other image-generating models like OpenAI's DALL-E 3 and Amazon's Titan Image Generator.
What sets Imagen 2 apart is its ability to generate text and logos in multiple languages, including Chinese, Hindi, Japanese, Korean, Portuguese, English, and Spanish.
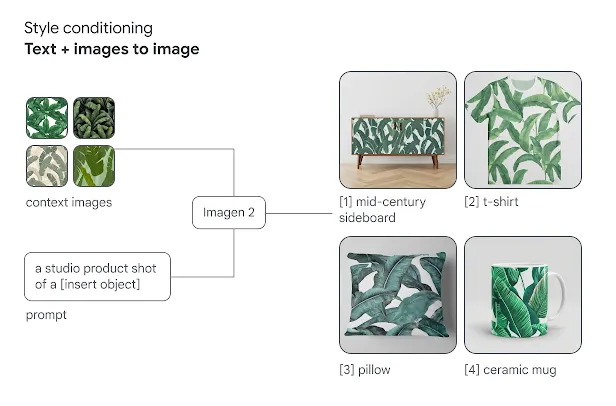
Utilizing diffusion-based techniques, Imagen 2 generating provides enhanced flexibility in controlling image styles. Reference style images, combined with a text prompt, allow users to condition Imagen 2 to generate new imagery aligned with specific styles.
Additionally, AI Imagen 2 introduces advanced image editing features like 'inpainting' and 'outpainting.' Users can seamlessly add or extend content in images, showcasing its versatility. This technology is slated for integration into Google Cloud's Vertex AI in the coming year.

SynthID, an approach developed by DeepMind, equips Imagen 2 AI with the ability to apply invisible watermarks to its creations. Google asserts that these watermarks are resilient to image edits, including compression, filters, and color adjustments. While Google provides a tool to detect these watermarks, it remains inaccessible to third parties, a move likely to address concerns over the proliferation of AI-generated disinformation.
However, Google's decision to withhold information about the data used for Imagen 2 training raises eyebrows. The legal landscape surrounding the use of publicly available or copyrighted data for commercial AI models is uncertain. Some AI companies, including OpenAI, offer opt-out mechanisms for contributors, while others like Adobe and Getty Images are working on compensation schemes.
Google, along with rivals like Amazon, currently lacks such mechanisms but provides an indemnification policy safeguarding eligible Vertex AI customers from copyright claims related to training data and Imagen 2 outputs.
As the landscape of AI-generated content evolves, the tech giant's move reflects an ongoing balance between innovation, legal considerations, and the concerns of content creators.
Interested in expanding your knowledge of technology and AI? Explore the latest news on Atlasiko!







